
|
|||||
|
|
| 基于氢化还原与端基钝化的老化沥青化学修复机制与性能评价 | |
| 作者姓名: | 陈辉强 雷笑秋 程俊 |
| 作者单位: | 1.重庆交通大学 土木工程学院, 重庆 400074;2.中建一局集团第五建筑有限公司,北京 100024 |
| 基金项目: | 国家自然科学基金资助项目(51708072)。 |
| 摘 要: | 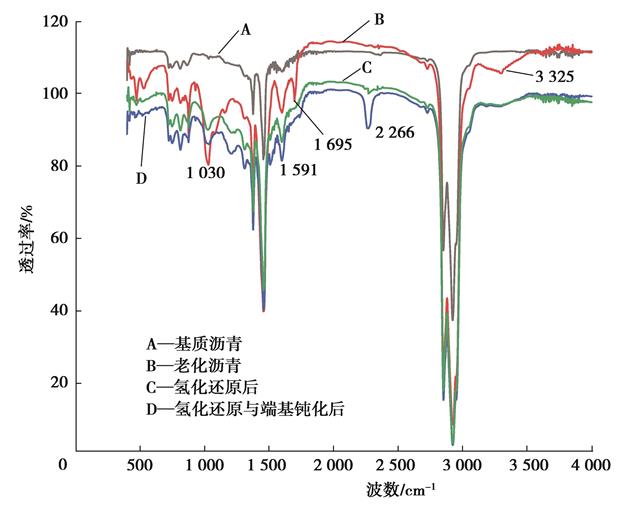 针对废旧沥青因性能劣化引起的再生沥青混合料路用性能不佳的问题,选用氢化还原剂三乙氧基硅烷将老化沥青中的强极性羰基和亚砜基还原成羟基,生成极性较低的酯或者醚;再通过端基钝化剂异氰酸酯与羟基进行酯化反应,实现端基钝化。通过测试老化沥青各修复阶段的微观化学结构与极性变化,研究其修复机理;进而以基质沥青为参比,分析测试老化沥青性能修复前后的动力粘度和低温性能,评价氢化还原与端基钝化对老化沥青的化学修复效果。 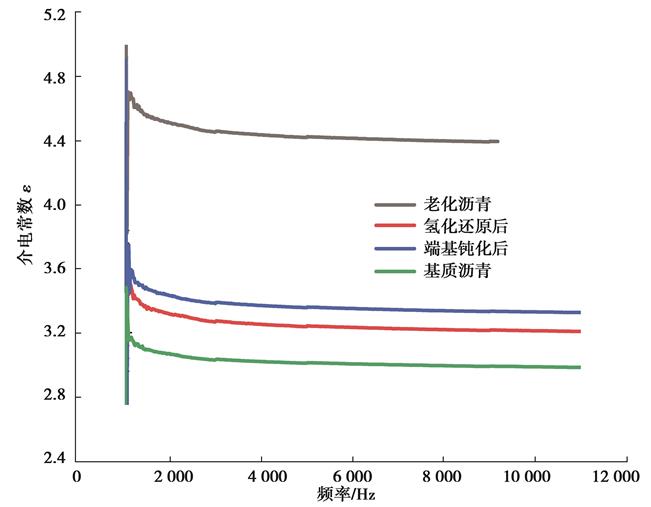 结果表明,氢化还原与端基钝化使老化沥青的化学结构发生了本质的变化,三乙氧基硅烷可将老化沥青中羰基和亚砜基还原成羟基,异氰酸酯可将羟基酯化成酯;经氢化还原与端基钝化之后,老化沥青的极性显著减弱,分子间作用力和粘度明显降低,低温变形能力得以显著改善,且老化沥青的低温性能与官能团指数之间具有良好的相关性。 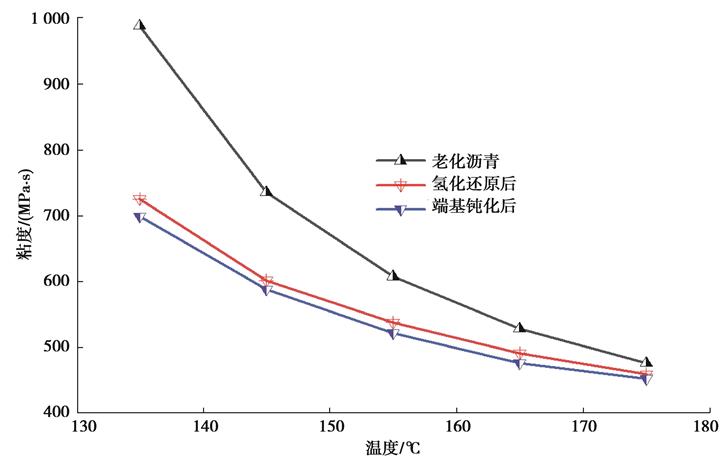 |
| 关 键 词: | 氢化还原 端基钝化 老化沥青 极性 动力粘度 低温性能 |
| 收稿时间: | 2022-08-30 |
| 点击此处可从《重庆大学学报(自然科学版)》浏览原始摘要信息 | |
| 点击此处可从《重庆大学学报(自然科学版)》下载全文 | |